Arthroscopic Surgery: A Game-Changer for Athletes and Active Individuals
Arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive surgical technique, has revolutionized the field of orthopedics, offering a less invasive and more efficient approach to diagnosing and treating a variety of joint disorders. This innovative procedure has become a crucial tool for athletes and active individuals seeking to recover from injuries and return to their active lifestyles.
Removing loose fragments: Loose fragments of bone or cartilage can cause pain and inflammation. Arthroscopic surgery can remove these fragments, restoring joint function.
Treating ligament tears: Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect bones and provide stability to joints. Arthroscopic surgery can repair or reconstruct torn ligaments.
Treating meniscal tears: The menisci are two C-shaped pieces of cartilage that provide cushioning and stability to the knee joint. Arthroscopic surgery can repair or remove torn meniscal tissue.
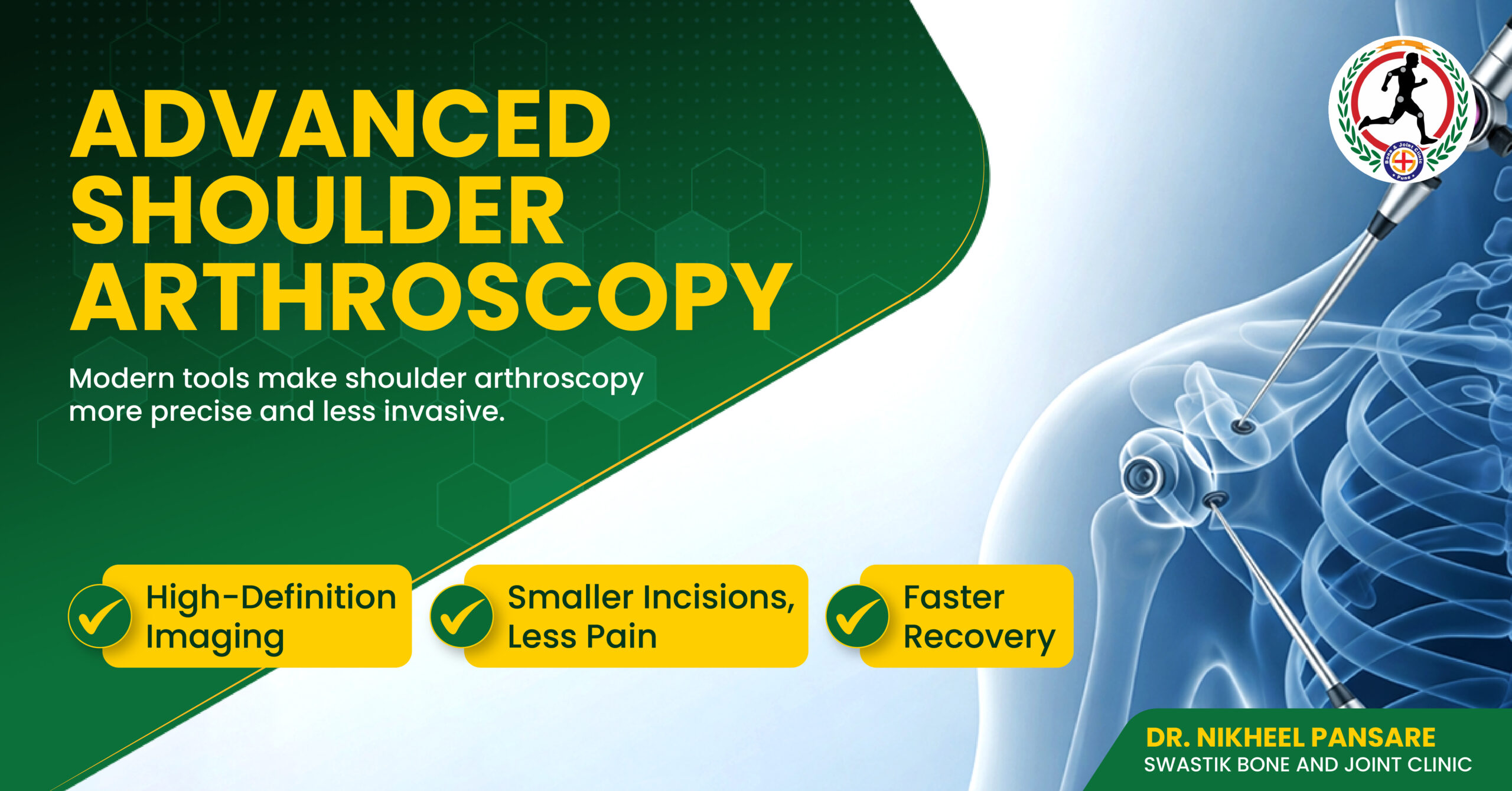
Minimally invasive: Smaller incisions result in less tissue damage, reduced pain, and faster recovery times.
Visualization: The arthroscope provides a clear view of the joint, allowing for precise diagnosis and treatment.
Outpatient procedure: In many cases, arthroscopic surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Reduced scarring: Smaller incisions lead to less noticeable scarring.
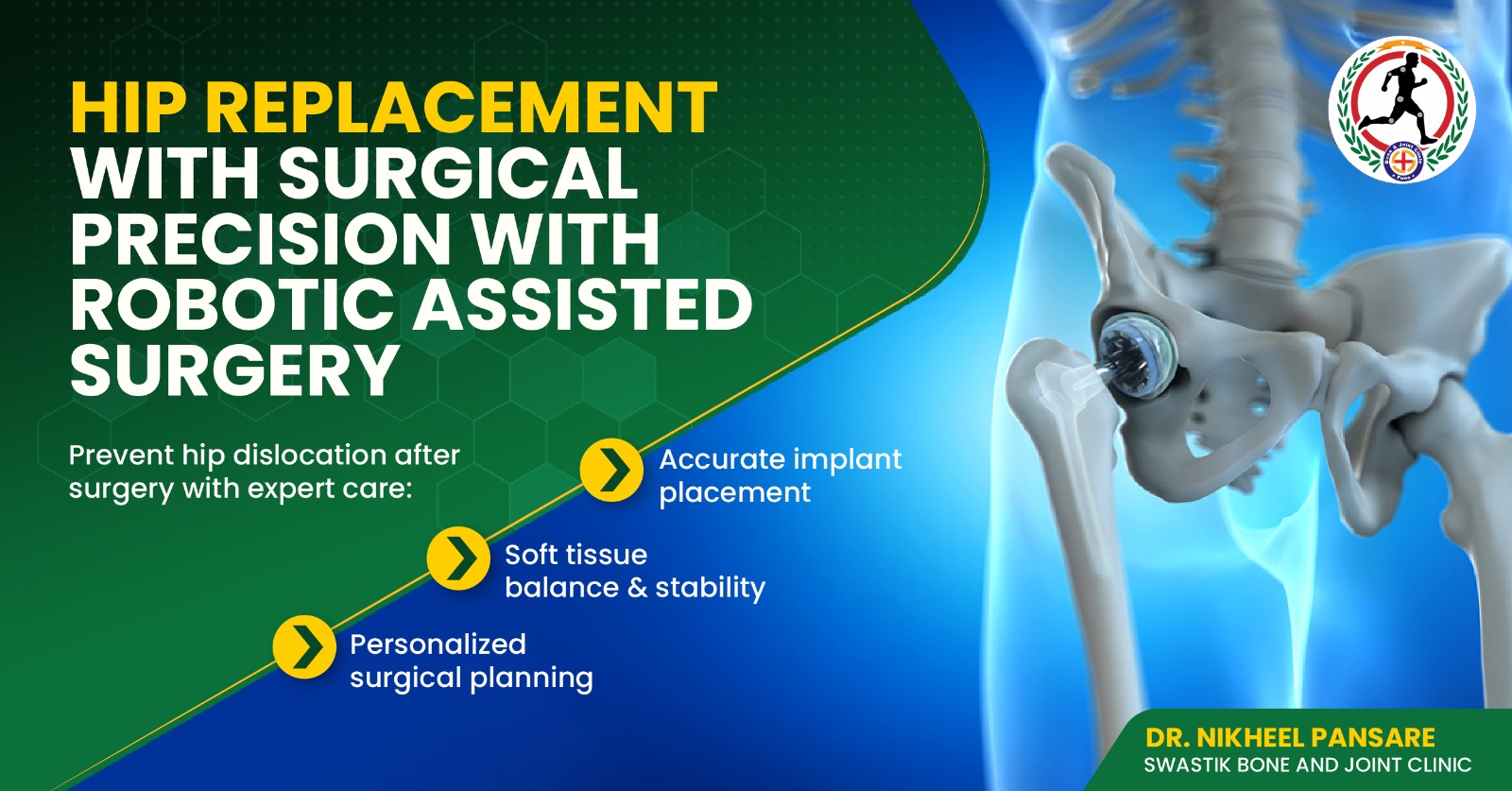
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears: The ACL is a major ligament in the knee that stabilizes the joint. Arthroscopic surgery can repair or reconstruct a torn ACL.
Meniscal tears: Arthroscopic surgery can repair or remove torn meniscal tissue.
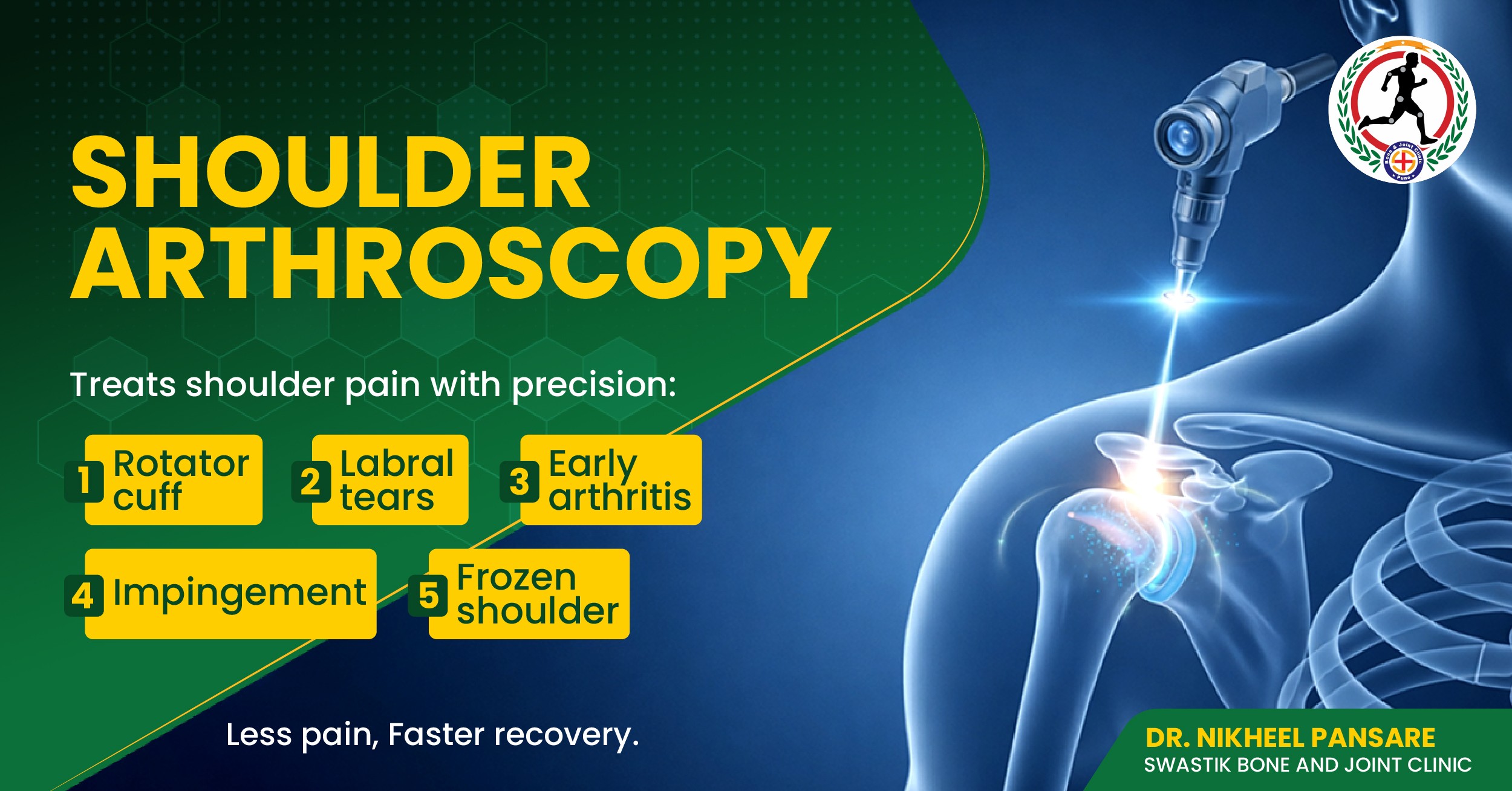
Rotator cuff tears: The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Arthroscopic surgery can repair torn rotator cuff muscles.
Shoulder impingement: Arthroscopic surgery can remove bone or tissue that is pinching or rubbing against tendons in the shoulder.
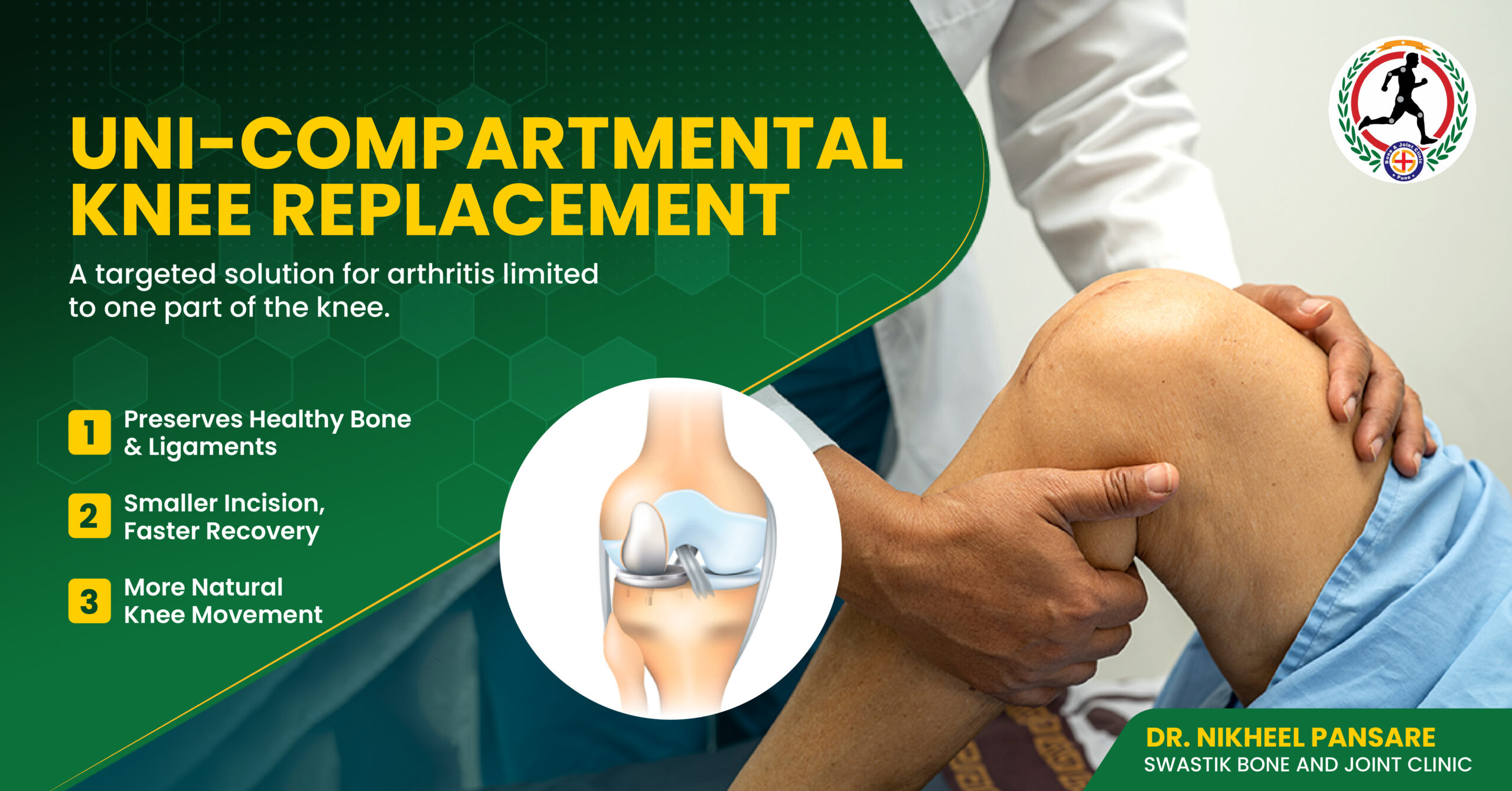
Cartilage degeneration: Arthroscopic surgery can repair or remove damaged cartilage.
Osteoarthritis: Arthroscopic surgery can remove debris and smooth out roughened surfaces in joints affected by osteoarthritis.
Joint pain: Arthroscopic surgery can diagnose the cause of joint pain and provide treatment options.
Understanding Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery involves inserting a thin, flexible tube called an arthroscope into a joint through a small incision. The arthroscope is equipped with a camera and light, allowing the surgeon to visualize the interior of the joint on a monitor. Specialized surgical instruments can be inserted through additional small incisions to perform various procedures, such as: Repairing torn cartilage: Cartilage is the shock-absorbing tissue that cushions the ends of bones in a joint. Arthroscopic surgery can repair torn cartilage fragments or smooth out roughened cartilage surfaces.Removing loose fragments: Loose fragments of bone or cartilage can cause pain and inflammation. Arthroscopic surgery can remove these fragments, restoring joint function.
Treating ligament tears: Ligaments are strong bands of tissue that connect bones and provide stability to joints. Arthroscopic surgery can repair or reconstruct torn ligaments.
Treating meniscal tears: The menisci are two C-shaped pieces of cartilage that provide cushioning and stability to the knee joint. Arthroscopic surgery can repair or remove torn meniscal tissue.
Benefits of Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:Minimally invasive: Smaller incisions result in less tissue damage, reduced pain, and faster recovery times.
Visualization: The arthroscope provides a clear view of the joint, allowing for precise diagnosis and treatment.
Outpatient procedure: In many cases, arthroscopic surgery is performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day.
Reduced scarring: Smaller incisions lead to less noticeable scarring.
Arthroscopic Surgery for Athletes
Arthroscopic surgery has become an essential tool for athletes, offering a faster and more effective approach to treating sports injuries. Common sports injuries that can be treated arthroscopically include:Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears: The ACL is a major ligament in the knee that stabilizes the joint. Arthroscopic surgery can repair or reconstruct a torn ACL.
Meniscal tears: Arthroscopic surgery can repair or remove torn meniscal tissue.
Rotator cuff tears: The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint. Arthroscopic surgery can repair torn rotator cuff muscles.
Shoulder impingement: Arthroscopic surgery can remove bone or tissue that is pinching or rubbing against tendons in the shoulder.
Arthroscopic Surgery for Active Individuals
Arthroscopic surgery is not just for athletes; it can also benefit active individuals who experience joint pain or injuries that limit their daily activities. Common conditions that can be treated arthroscopically include:Cartilage degeneration: Arthroscopic surgery can repair or remove damaged cartilage.
Osteoarthritis: Arthroscopic surgery can remove debris and smooth out roughened surfaces in joints affected by osteoarthritis.
Joint pain: Arthroscopic surgery can diagnose the cause of joint pain and provide treatment options.